In 2020, the Dome Fireplace swept by means of Southern California’s Mojave Nationwide Protect, blackening almost 70 sq. miles of extremely biodiverse desert. The conflagration killed 1.3 million Joshua bushes, together with most of these on Cima Dome, one of many largest and densest Joshua tree woodlands on this planet.
Then in 2023, the York Fireplace swept by means of and burned a big part of adjoining Joshua tree forest, killing one other million or so bushes. The destruction on Cima Dome — which is greater in elevation and cooler than the encompassing desert — got here as an particularly extreme blow to the Nationwide Park Service and conservationists who had thought of it a stronghold for the japanese Joshua tree and a key to the species’ future.
Specialists have been planning to make Cima Dome a refuge by clearing out invasive grasses and monitoring the woodland’s well being, stated Andrew Kaiser, a botanist who labored on the Mojave Nationwide Protect throughout the fires and now works for the California Division of Fish and Wildlife, creating its Western Joshua Tree Conservation Plan. “The perimeter of the 2020 Dome fireplace was primarily the precise define of the mannequin local weather refugia. It virtually fully overlapped it.”
Research discovered that if warming temperatures aren’t mitigated, almost one hundred pc of the bushes could possibly be misplaced within the coming a long time.
The variety of wildfires that kill and injury Joshua bushes has elevated sharply in recent times “in important half attributable to adjustments within the desert ecosystem,” stated Brendan Cummings, the conservation director of the Middle for Organic Variety, who lives within the city of Joshua Tree and is a frontrunner within the combat to legally defend the bushes. “Thirty years in the past, a typical fireplace in a Joshua tree woodland would burn lower than an acre. Lightning would hit a tree and it will fall. Not often wouldn’t it burn past an acre.” Now, he stated, bigger fires are prevalent.
Such blazes are one of many main threats to Joshua bushes: Hotter and drier climate, which kills seedlings and reduces recruitment of latest bushes, is one other necessary issue. Research from 2019 and 2011 discovered that if warming temperatures aren’t mitigated, almost one hundred pc of the bushes throughout their vary, which extends throughout elements of the southwestern United States, could possibly be misplaced within the coming a long time. That’s if growth, particularly of utility-scale photo voltaic farms, doesn’t wipe them out first.
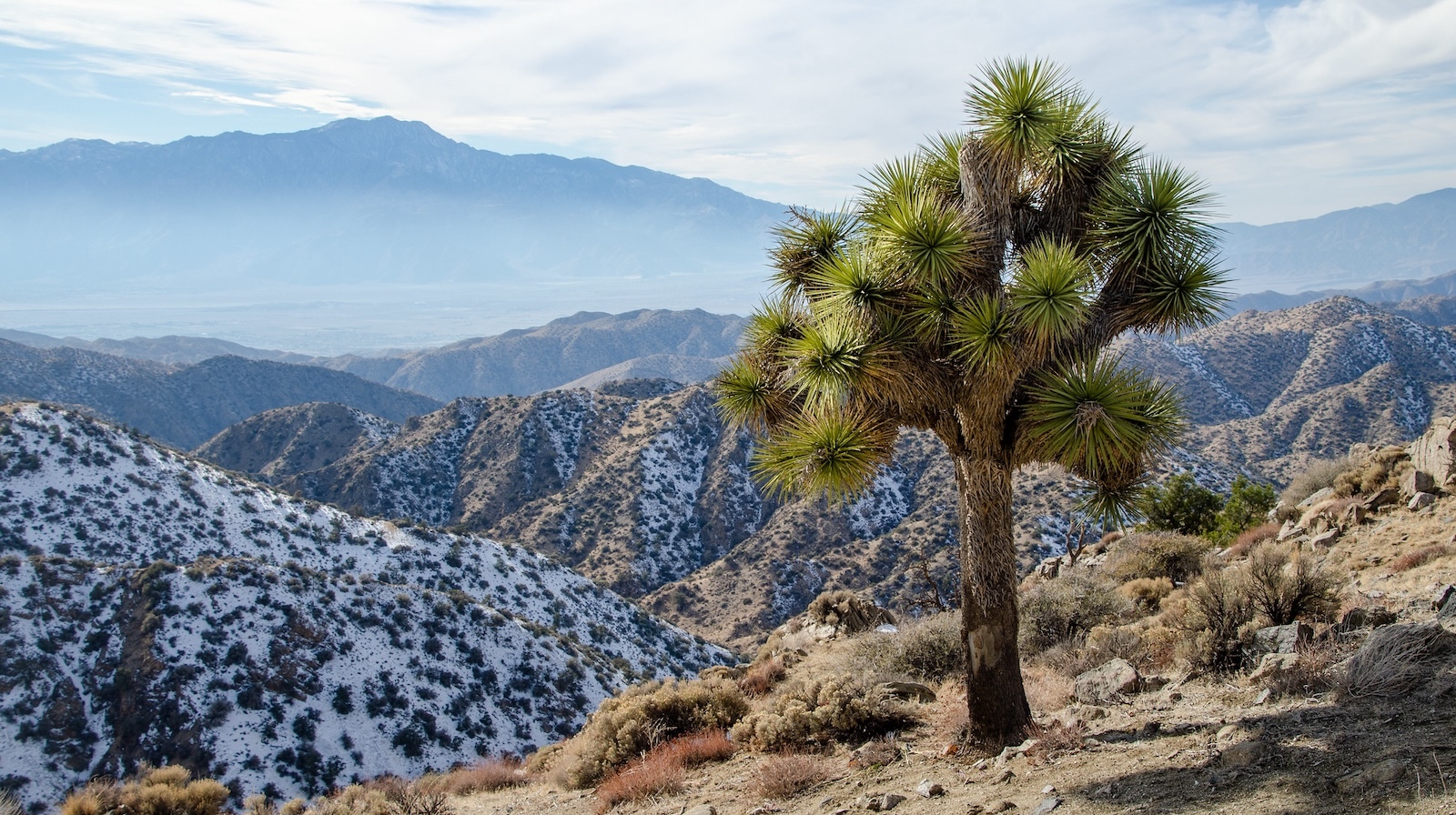
Joshua bushes are a species of yucca: With their shaggy bark and their balls of jagged leaves on the ends of crooked branches, they appear like one thing out of a Dr. Seuss e book. The Spanish known as them izote de desierto, the desert dagger, and the native Cahuilla tribe calls them humwichawa. Mormon settlers are stated to have named the tree after the prophet Joshua, who stored his fingers raised and unfold to information the Israelites. Mature bushes vary from 75 years outdated to greater than 300, and seedlings take about 30 years to succeed in maturity.
Yale Surroundings 360
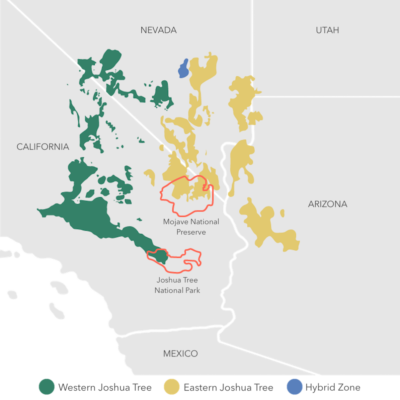
The Joshua tree has two distinct subspecies: the western Joshua tree, which happens largely in California — together with Joshua Tree Nationwide Park, a stronghold — and the japanese species, which is present in a lot of japanese California, southern Nevada, western Arizona, and in a small nook of Utah. Every is dependent upon a single species of moth for pollination — a moth that doesn’t pollinate the opposite species.
They’re additionally crucial to abandon biodiversity. “They’re keystone species, which suggests they create extra habitat for different species and enhance the biodiversity of the general desert,” stated Cameron Barrows, a retired College of California, Riverside, analysis ecologist who research Joshua bushes. “Every little thing from red-tailed hawks to nice horned owls to Scott’s orioles and cactus wrens — their density and abundance is tied to the provision of nesting websites, and Joshua bushes are actually the one nesting websites in a lot of the Mojave Desert.”
The desert night time lizard makes use of its fallen branches for shelter; the threatened desert tortoise consumes Joshua tree flowers; and the blacktail jack rabbit and desert wooden rat rely upon the water inside their trunk tissues.
Local weather change is a significant contributor to shifts within the Mojave’s fireplace regime. The huge enhance in acres burned is partly attributable to hotter temperatures, which enhance the expansion price of invasive grasses. The desert’s common temperature has gone up as a lot as 3.6 levels Fahrenheit (2 levels C) within the final hundred years, and rainfall has declined by as much as 20 p.c in some areas. Precipitation within the Mojave, essentially the most arid place in North America, varies broadly however averages 5 inches a 12 months. Joshua bushes are extremely tailored to the searing warmth of the Mojave, flourishing in temperatures of greater than 120 levels F (49 levels C). However they want moisture, too, and local weather change has introduced drought.

The York Fireplace burned roughly 1,000,000 Joshua bushes in Mojave Nationwide Protect in August 2023.
L.E. Baskow / Las Vegas Evaluate-Journal / Tribune Information Service by way of Getty Pictures
Local weather change is predicted to proceed to drive excessive swings in California’s climate within the coming years. And whereas a few current moist winters have helped new Joshua seedlings to sprout, their survival isn’t assured: Joshua bushes want a reliable provide of moisture to make it by means of their early years.
“The temperature is necessary, however rainfall is de facto necessary,” stated Barrows. “For those who couple greater temperatures and drier situations, you might be screwed.”
On the identical time, moist years additionally assist plant species that threaten the Joshua tree. “Over the previous few a long time, the invasive grasses initially introduced right here by cattle ranching and different sources have taken over the Mojave, [changing] the hearth regime,” stated Cummings. Grasses akin to purple brome and Mediterranean cut up grass are extremely flammable, and in moist years they develop in profusion and create extra intense and much more widespread fires.
There’s additionally concern that the invasion of unique species, together with local weather change and the deposition of atmospheric nitrogen — which wafts in from the smoggy Los Angeles basin and stimulates the expansion of flammable grasses — will preserve the post-fire Joshua woodlands from reestablishing themselves. As an alternative, these areas might convert to a non-native grassland with low biodiversity.
Satirically, one of many largest threats to bushes are large-scale photo voltaic arrays which might be being constructed to assist wean California off fossil fuels.
The western Joshua tree has been proposed for threatened standing below the California Endangered Species Act and has been regulated, since 2023, by the state’s Western Joshua Tree Conservation Act, which forbids reducing bushes from both non-public or public land with out authorization from the state. The federal authorities, below each the Trump and Biden administrations, rejected federal endangered species safety for each subspecies, most lately in 2023.
One motive for the shortage of safety is that there’s at present no scarcity of Joshua bushes — the menace relies on projections of future loss. The inhabitants of japanese Joshua bushes is estimated to be a number of million, and the western inhabitants comprises as many as 10 million bushes. Nonetheless, Cummings argues that they’re each deserving of safety as a result of the forecasts of the longer term look bleak. “We all know they’re on an extinction trajectory, given the specter of local weather change,” he stated. “If local weather change is frozen at present ranges, we [still] lose half their vary.” Temperatures, in fact, are usually not anticipated to stay regular.
One other potential menace to the western species is growth within the Mojave Desert, the place half of the bushes happen on non-public land. (The overwhelming majority of japanese Joshua bushes develop on public land.) Satirically, one of many largest threats to bushes are large-scale photo voltaic arrays which might be being constructed to assist wean the state off fossil fuels. The 530-megawatt Aratina solar-plus-storage mission, to be constructed on non-public land close to Boron, California, would kill almost 4,000 Joshua bushes and cut back habitat for desert tortoises and different species.

The desert tortoise, red-tailed hawk, and black-tailed jackrabbit all rely upon Joshua bushes.
Daniel Elsbrock / NPS; Preston Jordan Jr. / NPS; Brad Sutton / NPS
Photo voltaic builders oppose itemizing the tree as threatened. The California desert, together with the North African desert, has the best photo voltaic radiance on this planet, they argue, which makes it prime for producing electrical energy. “Our grid capability must be expanded by numbers which might be virtually unimaginable,” Shannon Eddy, govt director of the Giant-Scale Photo voltaic Affiliation, instructed Vice Information. “We’re simply on the very forefront of figuring this out. So to take big swaths of the desert and set them off limits to photo voltaic growth now, earlier than we actually know the place they should go, isn’t acceptable.”
The Western Joshua Tree Conservation Act, which grandfathered in some photo voltaic initiatives, took place when the California Division of Fish and Wildlife deadlocked on whether or not to record the subspecies as threatened. A political compromise, the act handed as a result of it supplied extra administration flexibility than itemizing the tree.
The act requires the Division of Fish and Wildlife to create — with different governmental businesses, California Native American tribes, and the general public — a draft conservation plan for the species by December 31, 2024, and it requires firms to purchase permits to chop down or relocate Joshua bushes. Charges for permits might be used to create a conservation fund. The plan goals to guard not solely the tree, however the bigger Mojave Desert ecosystem — together with bushes, the desert tortoise, burrowing owls, uncommon vegetation, yucca moths, and different species — from the crush of growth.
“It’s certainly not excellent,” stated Cummings. “However it can deliver issues right into a rational, orderly, and lawful house. Excessive desert communities have actually carried out a horrendous job of defending the desert panorama from growth.”

Drew Kaiser, a botanist with the Nationwide Park Service, inspects invasive purple brome grass in Mojave Nationwide Protect.
Irfan Khan / Los Angeles Instances by way of Getty Pictures
One key a part of the rising conservation technique, which is guided partly by a current paper revealed within the journal Organic Conservation, is to guard the bushes in refugia, designated areas the place the Joshua tree forest is wholesome and that is likely to be cooler and fewer prone to drought as temperatures enhance. In Joshua Tree Nationwide Park, managers are clearing grasses in refugia, for instance, to take away gas and create fireplace breaks between bushes.
Researchers are additionally mapping the bushes’ genomes to foretell which populations are most resilient to warmth and drought so their preservation may be prioritized or their seeds used for replanting.
Assisted migration — bodily shifting grownup bushes to Northern California and Oregon — has been thought of. However “you’ll be able to’t simply transfer the Joshua tree,” Kaiser, from California’s Division of Fish and Wildlife, stated. “You’ve acquired to maneuver the nurse vegetation [which help seedlings get established]. You’ve acquired to maneuver the yucca moth pollinator. You’ve acquired to observe. The entire analysis we’ve seen thus far suggests it’s not a viable choice at this second in time. However we’re not ruling it out.”
Regardless of all these threats, there are glimmers of hope. Elevated use of electrical automobiles in Southern California, for instance, might cut back ranges of the atmospheric nitrogen that fuels the expansion of flammable grasses.
And there may be widespread dedication by involved companions. “In areas which might be nicely managed, like a nationwide park, I’m optimistic,” stated Barrows, of UC Riverside. “Curiously, there are some areas the place bushes are literally invading up into the pine forest and doing very well as a result of it’s greater, cooler, and wetter. So Joshua bushes as a species are usually not going to go extinct, however areas of the Mojave Desert will grow to be extra ecologically depauperate in the event that they lose the Joshua tree — until we will reverse the local weather change subject.”
